

Relative Clauses عبارات الوصل
•يستخدم ضمير الوصل لربط جملتين و يحل محل اسم أو ضمير موجود غالبا في الجملة الثانية:
•تستخدم who لتحل محل الفاعل أو المفعول. أما whom فتحل محل المفعول فقط و غالبا تستخدم مكانها who:
• The boy looks very tired. He ran a long way. (who)
The boy who ran a long way looks very tired.
• The woman was put in jail. The police charged her with murder.
The woman who (whom) the police charged with murder was put in jail.
• تستخدم which لتحل محل الفاعل و المفعول غير العاقل:
• The job was very tiring. He applied for it a week ago.
The job which (that) he applied for was very tiring.
•تستخدم whose للملكية.
• The man felt very sad. His wife died in the accident.
The man whose wife died in the accident felt very sad.
•لاحظ أن هناك نوعان من عبارات الوصل ، النوع الأول يعطي معلومة أساسية عن الشيء أو الشخص أو المكان الذي نتحدث عنه ونستخدم في هذا النوع who / which / whom ولا نستخدم comma قبل أو بعد عبارة الوصل. ويمكن استخدام that بدلا من ضمائر الوصل المذكورة .
•The company which he works for sells computer.
• The woman who killed her husband was sentenced to death. حكم عليها بالإعدام
•والنوع الثاني لا تقدم عبارة الوصل معلومة هامة عن الشيء أو الشخص أو المكان الذي نتحدث عنه ولا بد من استخدام comma قبل وبعد عبارة الوصل و لا تستخدم that في هذا النوع:
• Mr. Ahmed, who has just arrived, is a famous politician.
• The company, which is in Cairo, employs 200 people.
•لاحظ أن that / who لا يسبقهما حرف جر:
The man for whom he works is German.
The man that he works for is German.
The man who / whom he works for is German.
•لاحظ استخدام that بعد صفات التفضيل للإشارة إلي غير العاقل:
•وفي حالة وجود عاقل مع صفات التفضيل يمكن أن نستخدم that أو who:
This is the best book that I have ever read.
He was the best king that / who ever sat on the throne. العرش
•عادة تستخدم that بعد الكلمات الآتية:
All / much / little (that)
All the apples that fall are eaten by the goats.
• لاحظ في الجملة الآتية أنه لا يمكن استخدام that بدلا من which إلا إذا وضعنا حرف الجر بعد الفعل :
• The house cost him a lot of money. He lived in it.
The house in which he lived cost him a lot of money.
The house that he lived in cost him a lot of money.
What = the thing that / the things that
• The things that we saw astonished us. = What we saw astonished us.
• The thing that annoys him is that his friend always comes late.
= What annoys him is that his friend always comes late.
يمكن استخدام to + inf. بدلا من عبارة الوصل اذا كان ضمير الوصل في الجملة يحل محل الفاعل وفي حالة وجود ما يلي :
The first / second/last/only
• Ali was the first student who arrived at school.
= Ali was the first student to arrive at school.
• He was the last man who left the ship.
= He was the last man to leave the ship.
لاحظ تركيب الجملة الآتية:
It + is / was + اسم + who / that …
It + is / was + اسم + which / that …
It was Peter who broke the window.
It was the bus that delayed us.
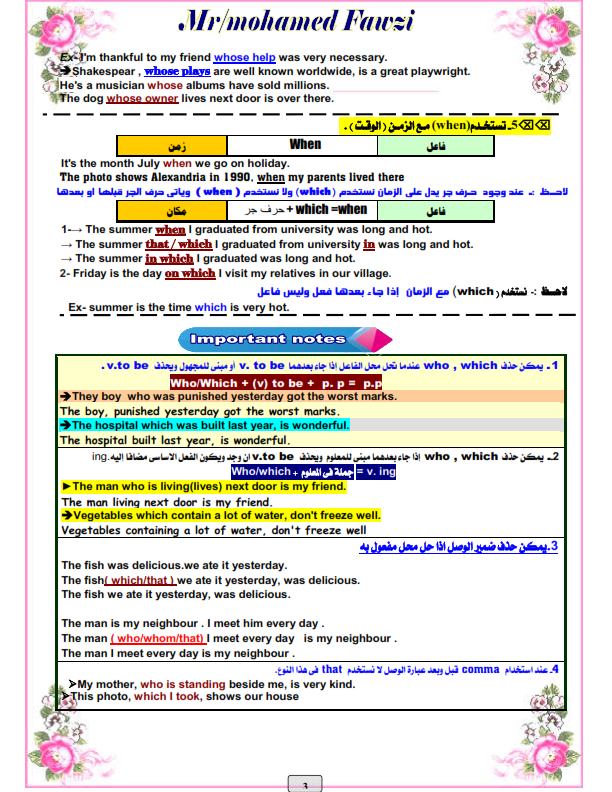
• يمكن حذف ضمير الوصل في الحالات الآنية (مع ضرورة حذف TO BE أيضا):
• إذا كان بعده مبنى للمجهول :
• The man ran away. He was arrested for murder last month.
The man who was arrested for murder last month ran away.
The man arrested for murder last month ran away.
• أو إذا كان بعده جار و مجرور (حرف جر واسم):
• The boy wants to borrow some books. He is in the library.
The boy (who is) in the library wants to borrow some books.
• أو إذا كان بعده اسم أو صفة بعدها اسم:
• John Smith was interviewed on TV. He is a famous runner.
John Smith, (who is) a famous runner, was interviewed on TV.
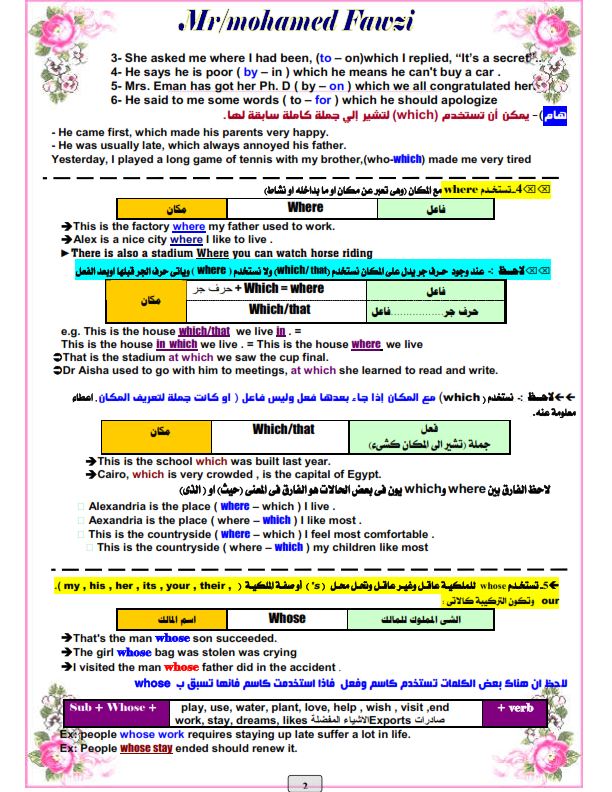
•تستخدم where بدلا من which و حرف جر إذا كانت تدل على مكان أو بدلا من there
• The shop was so big. He worked in it. (which / where)
The shop which he worked in was so big.
The shop where he worked was so big.
• He went to Acapulco. He spent most of his holiday there.
He went to Acapulco where he spent most of his holiday.
•تستخدم when بدلا من which و حرف إذا كانت تدل على زمن:
• The day was remembered for long. They met on it.
The day on which they met was remembered for long.
The day when they met was remembered for long.
•لابد من استخدام ضمير الوصل إذا جاء في مكان الفاعل و بعده الفعل:
•إذا حذف ضمير الوصل و كانت الجملة معلوم Active نستخدم :V.+ ING
• The man is very kind. He works in this office.
The man who works in this office is very kind.
The man working in this office is very kind.
• يمكن حذف ضمير الوصل إذا جاء مكان المفعول:
• The officer treated me very well. I met him at the police station.
The officer whom/ who/ that I met at the police station treated me very well.
The officer I met at the police station treated me very well.
Language Notes:
•في حالة وجود اسمين يجمع الثاني ويعامل الأول كصفة ولا يجمع:
a car factoryمصنع سيارات two car factories
a door knob مقبض الباب three door knobs
Everyday (adj.) يوميا
Every day (adv.) كل يوم
• We face a lot of problems in our everyday life. كل يوم
• I go to school every day. يوميا
•الكلمات الآتية تعامل معاملة المفرد بالرغم من أنها تنتهي بحرف s:
Economics علم الاقتصاد – statistics علم الإحصاء
mathematics الرياضيات – physics الفيزياء
• Economics is sometimes hard to understand.
affect = have an effect on
•عند استخدام effect بدلا من affect يتغير زمن have حسب زمن الفعل الأساسي للجملة:
•The storm affected the roads badly. (effect)
The storm had a bad effect on the roads.
•The accident has affected her deeply. (effect)
•The accident has had a deep effect on her.
•هناك كلمات تأتي أحيانا بعد كلمة :chief
chief buyer المشتري الرئيسي chief engineer كبير المهندسين
be made of مصنوع من مادة لا تتغير
This handbag is made of plastic.
be made from مصنوع من مادة أو أكثر تتغير
Bread is made from flour and water.
be made in (a country)
We should encourage products that are made in Egypt.
be made by مصنوع بواسطة
This table was made by a clever carpenter.
Most = nearly all / almost all
•Most students passed the test. = Nearly all students passed the test
•لاحظ الفرق بين الكلمات الآتية:
Wages – salary – fare – fees
Wages أجور (عمال مثلا) بالساعة أو اليوم أو الأسبوع
• The workers went on strike because they wanted higher wages.
Salary مرتب شهري أو سنوي
•This bank manager gets a salary of 40,000 dollars a year.
Fare أجرة مواصلات Taxi fare bus fare plane fare
Fees رسوم أو أتعاب lawyer's fees school fees رسوم مدرسية
•Doctors' fees are very high nowadays.
afford + to + inf. .لديه من المال ما يمكنه من شراء ...
afford + n.
•I can’t afford to buy a new car.
• I wish I could afford a new computer.
hire يستأجر(عادة لفترة قصيرة)/ يوظف
•We hired a car for a week.
•The company hired a new secretary.
hire out يؤجر
• Why don't you hire out your car to your neighbours while you are away and make some money?
Rent : (a flat / an office / a building) يستأجر لفترة طويلة
Look forward to + v-ing / n.
• I look forward to visiting London.
• I am looking forward to my holiday.
Be located in = be situated in للتعبير عن موقع مكان في دولة أو قارة مثلا
Be located on = be situated on للتعبير عن الموقع علي بحر أو نهر أو محيط
•The office is located in the city center.
•The town is situated on the Mediterranean Sea.
Start with = begin with + n.
Start by = begin by + v-ing
• Let's begin with exercise B.
• He started his speech by telling us something about his life.
